Posted by Simon Long Jan 26, 2021
Getting Started With Oracle Cloud VMware Solution (OCVS) – Connecting To An On-Premises Environment
In my recent ‘Getting started with Oracle Cloud VMware Solution (OVCS)’ post; Getting Started With Oracle Cloud VMware Solution (OCVS) – Connecting To Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Services we deployed a Windows Server into our OCVS SDDC and connected it, using NFS, to an OCI File System that will be used to store files and folders for our users.
Posts in this series:
- Deploying A Bastion Host
- Deploying The SDDC With HCX
- Deployment Overview
- Networking Configuration
- Connecting To Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Services
- Connecting To An On-Premises Environment
- Migrating Workloads Using VMware HCX
In this blog post, we are going to look at connecting our OCVS SDDC environment to our on-premises vSphere environment, so that our workloads in both environments can communicate with each other. There are two main ways of connecting OCVS to an on-premises environment. Oracle FastConnect or Oracle VPN Connect. In my environment, I will be using an Oracle FastConnect connection provided by Megaport. As there are many other ways of setting up a FastConnect via other services, I will not document that section step-by-step.
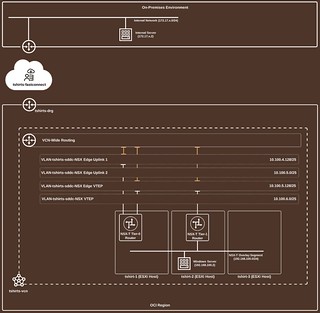
Here is a high-level diagram of what we are going to be configuring.
Create A Dynamic Routing Gateway
The first step to enabling hybrid connectivity is to deploy a Dynamic Routing Gateway (DRG) within our Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). You can think of a DRG as a virtual router that provides a path for private traffic (that is, traffic that uses private IPv4 addresses) between your VCN and networks outside the VCN’s region.
- Login to the OCVS console
- Select the correct Region. (This should be the same region that the SDDC and the Bastion host were deployed)
- Click on the burger icon at the top left of the screen to display the menu
- Select Networking > Dynamic Routing Gateways

-
- Click Create Dynamic Routing Gateway
- As always, select the correct Compartment
- Name the DRG (I used tshirts-drg)
- Click Create Dynamic Routing Gateway
Once the DRG has been created, we now need to attach it to our VCN.
- Click Virtual Cloud Networks on the Resources section (left-hand side)
- Click Attach to Virtual Cloud Network
- Select your VCN in the dropdown
- Click Attach to Virtual Cloud Network
Create A FastConnect
Before we can create our FastConnect connection, we need to collect some information that will be used as part of this process.
-
- BGP IP Addresses: You’ll need two IP Addresses to use for the BGP connection between the FastConnect and your on-prem or cloud router. Typically, Link-Local Addresses are used for this.
- Customer BGP ASN: You’ll need your Autonymous System Number (ASN) If you are using a service like Megaport, your ASN can be found in the portal. If you are just using an on-premises router, you can usually choose an ASN from the private range: 64512 – 65534. If you aren’t sure about what to use here, speak to your networking team.
-
-
- Click on the burger icon at the top left of the screen to display the menu
- Select Networking > FastConnect
- Click Create FastConnect
- Select your Connection Type (I selected Partner as I am using Megaport)
- If you selected FastConnect Partner, select your Partner from the dropdown
- Click Next
- Click Create FastConnect

-
-
- Name the FastConnect Connection (I used tshirts-fastconnect)
- Select Private Virtual Circuit
- Select your Dynamic Routing Gateway from the dropdown
- Select the Bandwidth for the connection
- Enter the Customer BGP IPv4 Address
- Enter the Oracle BGP IPv4 Address
- Enter the Customer BGP ASN
- Click Create
-
-
Configuring BGP On-Premises
Now that you have created your Oracle FastConnect, next, we need to configure the on-premises router to establish a BGP session. The steps that are needed to perform this configuration will vary depending on which router or service you are using for your on-premises connectivity. For this reason, I am not going to document the step-by-step process. For my Megaport connection, I followed the Connecting to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect documentation.
However, the information I needed to complete the configuration can be found in one place in the OCI interface.
-
-
- Click on the burger icon at the top left of the screen to display the menu
- Select Networking > FastConnect
- Click the name of the FastConnect Connection you just created
- Click the BGP Information tab
- Click the name of the FastConnect Connection you just created
-
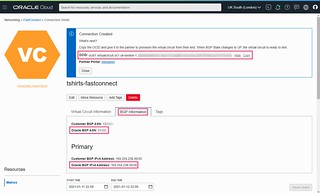
The information you are looking for is as follows:
-
-
- FastConnect OCID (This is often required by services such as Megaport)
- Oracle BGP ASN
- Oracle BGP IPv4 Address
-
With this information to hand, go ahead and configure the BGP configuration. Once correctly configured, the OCI console will appear green, Lifecycle State will show as Provisioned and the IPv4 BGP Status will show as UP.

Configure Route Tables and Network Security Groups
With our on-premises connectivity established, it’s time to configure our OCI environment to allow traffic to flow between our on-premises environment and our Windows Server virtual machine running within our OCVS SDDC.
Luckily for us, Oracle Cloud provides us with a simple wizard that creates the required configuration automatically for us. Thanks, Oracle!
-
-
- Click on the burger icon at the top left of the screen to display the menu
- Select VMware Solution
- Click the name of your OCVS SDDC
-
-
-
-
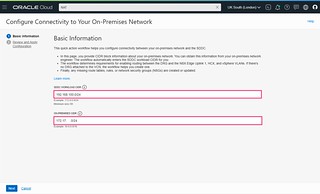
- Click Configure connectivity to your on-premises network
- Enter the CIDR Block of the workload overlay network (In this example I am using 192.168.100.0/24)
- Enter the CIDR Block of the on-premises network that you want to connect to
- Click Next
-
-
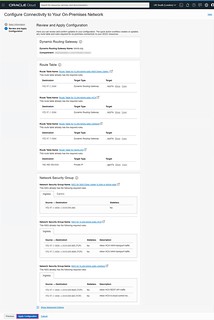
-
-
-
- Review the configuration
- Click Apply Configuration
-
-
The cool thing about the review page is that it displays exactly what Route Table and Network Security Group configurations the wizard is going to make. I found this very useful to help me understand how Route Tables and NSG’s need to be configured to allow traffic to flow. This knowledge will help me in the future when I need to configure something that Oracle doesn’t offer a wizard for.
NOTE: By default, the wizard allows ALL traffic between the on-premises network and the workload network. If this is not desired, be sure to change the rules configured on the following NSG: ‘NSG for NSX Edge Uplink VLANs in tshirts-sddc’
Testing Connectivity
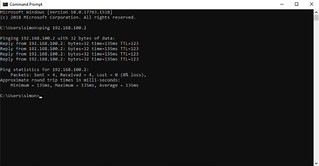
All that is left is to make sure connectivity is working between our on-premises environment and our Windows server which is running in our OCVS SDDC.
The quickest and easiest way to test this is to run a simple ping from a server running in the on-premises environment to a server running in OCVS. Remember, Windows blocks ping by default, so allow it through the windows firewall if you haven’t already.
Summary
In the blog post, we’ve been able to quickly and easily configure hybrid connectivity between our on-premises environment and our OCVS SDDC. In my experience, the part the causes the most issues is the BGP configuration. So if you aren’t already, I’d recommend speaking to someone from your networking team who can assist you. It’s a very simple configuration IF you’ve previously configured BGP.
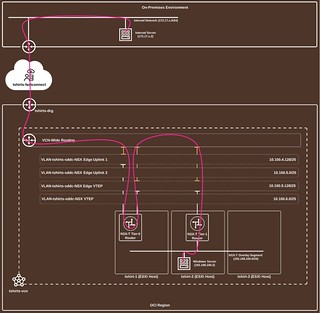
Traffic flowing from our on-premises virtual machine exits the on-premises router via its BGP connection which is established with the Oracle FastConnect. Traffic then enters the Oracle Cloud infrastructure via the Dynamic Routing Gateway and is sent to the ‘VLAN-tshirts-sddc-NSX Edge Uplink 1’ VLAN where it enters the NSX Edge vIP. The NSX-T Tier-0 router forwards the traffic to the Tier-1 router which sends the traffic to the Windows server connected to the workload Segment.
In the next post in this ‘Getting Started with Oracle Cloud VMware Solution (OCVS)’ series, we’ll be looking at using VMware HCX to migrate workloads from our on-premises network over to our OCVS SDDC.
